Biodiversity in Kenya

Biodiversity or biological diversity is the diversity of life, meaning plant and animal species richness and abundance in an area. Biodiversity is commonly identified at three levels.
- Genetic diversity is the diversity of genes within a species. Genetic variability exists among the populations and individuals of the same species.
- Species diversity or diversity among species in an ecosystem. "Biodiversity hotspots" are excellent examples of species diversity.
- Ecosystem diversity, diversity at a higher level of organization, the ecosystem. This has to do with the variety of ecosystems on Earth.
Kenya is a mega bio-diverse country with over 35,000 species of flora and fauna. Insects dominate the species diversity. This diversity is served by the variable ecosystems ranging from marine, mountains, tropical, drylands, forests, and arid lands. In addition to these are some 467 inland lake and wetland habitats covering about 2.5% of the total area. Kenyan forests are endowed with a rich array of plant and animal life. Some of the species endemic to the forest habitats are found nowhere else in the world. Since species richness tends to correlate with the annual rainfall, wetter forests are richer in species. Consequently, Kakamega Forest has the richest plant diversity in Kenya. However, coastal forests have more value as centers of endemism with many plant and animal species found nowhere else in the world.
Kenya covers a land area of approximately 583,000 square kilometers. Kenya straddles the Equator between approximately 4.5 degrees South and 4.5 degrees North latitude. With a coastline of approximately 640 km, the total area of the Kenyan Marine Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) extending 200 nautical miles is about 230,000 square kilometers. Thus, by area, about 28% of Kenya’s ecosystems are marine and 72% are terrestrial. About two thirds of Kenya’s land is less than 900 meters above sea level and one third is comprised of highlands. The highlands, mainly in south-western Kenya, surround five major areas of mountains or hill ranges (Mount Kenya, Mount Elgon, the Aberdares Range, the Mau Escarpment, and the Cherangani Hills). The Great Rift Valley, stretching north- south across the country, splits the highlands into a western and eastern part. The Rift Valley contains numerous closed basin saline lakes and some freshwater lakes, including Lake Naivasha and Lake Baringo in the eastern branch of the Rift, and Lake Victoria, which lies between the two Rift branches. Freshwater and saline ecosystems cover about 8% of Kenya, including rivers, lakes and wetlands with Lake Victoria, Lake Turkana, Lake Naivasha, and Lake Baringo being the four largest inland water bodies.
Kenya is endowed with diverse ecosystems and habitats that are home to unique and diverse flora and fauna. . Kenya’s rich biodiversity can be attributed to a number of factors, including a long evolutionary history, the country’s varied and diverse habitat types and ecosystems, diversity of landscapes and variable climatic conditions. About 70% national biodiversity resources are found outside the protected, while the 30% are within protected areas that include national parks, reserves, sanctuaries, gazetted forests, and heritage forests.
Kenya is rich in biological diversity. Around 25,000 species of animal and 7000 species of plants have so far been recorded, along with at least 2000 fungi and bacteria. An enormous species of plants and animals inhabit the country’s varied habitats, from its crowded and colorful coral reefs to icy alpine moorlands.

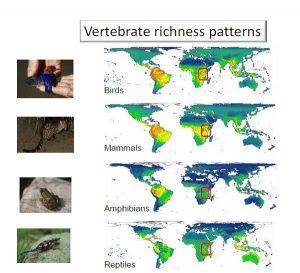
Vertebrates richness patternsViewed in Global perspective, eastern Africa is biodiversity-rich in terrestrial vertebrates, especially mammals and birds. Eastern Africa is shown in the red box. Orange and red areas indicate areas of high species richness, green and blue areas of low richness. Source: Walter Jetz.Biodiversity Atlas Kenya
Plant biodiversity
The Kenyan vascular plants diversity consisting of 7004 species comprises 1720 genera and 240 families.
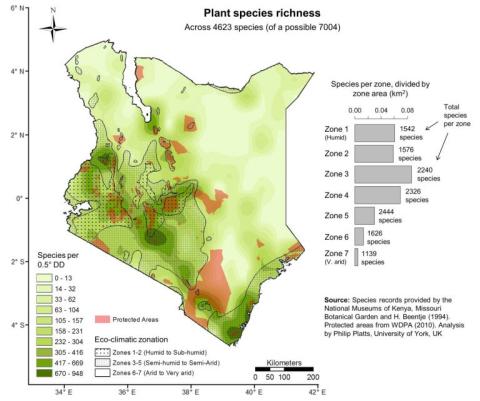
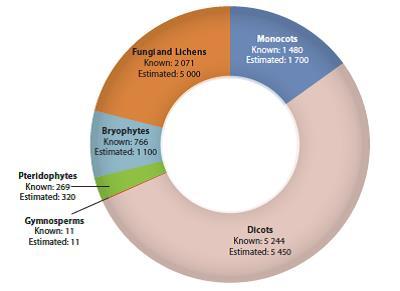
Plant and fungi diversity in Kenya Kenya's 7 004 vascular plants comprise 1 720 genera and 240 families. The plant families are dominated by angiosperms (flowering plants), most of which are legumes (708 species) and grasses (576species). Other species-rich families are the Compositae (494), Euphorbiaceae (341), Rubiaceae (330),Orchidaceae (249), Acanthaceae (225), Labiatae (218) and Cyperaceae (211). Source: NMK, Biodiversity Atlas Kenya
Key Platforms for Plant Conservation in Kenya:
4. The East African Herbarium (EA Herbarium)
- Website: EA Herbarium
- Focus: The East African Herbarium, part of the National Museums of Kenya, works on the collection and identification of plant species across East Africa. It contains a wealth of plant specimens, many of which are indigenous to Kenya.
- Key Functions: Plant species research, identification, and cataloging for biodiversity studies and conservation efforts.
5. Kenya Indigenous Vegetables Network (KIVINET)
- Website: KIVINET
- Focus: KIVINET promotes the conservation and cultivation of indigenous vegetable species in Kenya. Their platform focuses on the dissemination of knowledge regarding indigenous plants and their nutritional, medicinal, and economic value.
- Key Functions: Promoting the use and conservation of indigenous vegetables, conducting research on their ecological benefits, and engaging in sustainable agricultural practices.
6. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) - Kenya
- Website: IUCN Kenya
- Focus: While IUCN is a global organization, the Kenya office works on various biodiversity conservation projects, including those related to plants. The organization’s Red List of Threatened Species includes plant species found in Kenya, providing a global overview of threatened flora.
- Key Functions: Threat assessment, plant species conservation, habitat restoration, and promoting sustainable land use practices.
7. Kenya Biodiversity Information System (KBIS)
- Website: KBIS
- Focus: KBIS is a platform that aims to compile and share data on Kenya’s biodiversity, including plants, animals, and ecosystems. It provides a database where researchers and the public can access information on species found in Kenya, including details on their conservation status.
- Key Functions: Biodiversity data sharing, research, and tracking species distributions across Kenya, including plants.
8. The Flora of East Africa (FEA) Project
- Website: Flora of East Africa
- Focus: This project aims to catalog and document plant species in East Africa, including Kenya. It is a joint effort between Kew Gardens and other botanical institutions. It provides a comprehensive guide to the flora of the region, including information on plant species diversity, conservation, and uses.
- Key Functions: Plant species identification, documentation, and conservation; public access to botanical information.
9. Tree Seed Centre (TSC) – Kenya Forestry Research Institute (KEFRI)
- Website: KEFRI
- Focus: KEFRI focuses on the research, conservation, and propagation of forest trees and other indigenous plants. The Tree Seed Centre within KEFRI provides a platform for the collection and distribution of indigenous tree seeds for afforestation, reforestation, and conservation.
- Key Functions: Indigenous tree conservation, seed banking, and promoting the use of native plants for ecological restoration.
10. Kenya Plant Conservation Network (KPCN)
- Website: KPCN
- Focus: KPCN is an initiative aimed at the conservation of Kenya’s plant species, especially those at risk. The network works on monitoring, research, and raising awareness about the importance of plant conservation in Kenya.
- Key Functions: Plant species conservation, raising awareness about endangered plants, and promoting conservation best practices.
Animal Biodiversity
Kenya retains a remarkable variety of globally important and locally valuable flagship animal species. These include birds, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, fish and invertebrates. The diversity of Kenya's wildlife has garnered international fame.Animal biodiversity hold medicinal, agricultural, ecological, commercial, aesthetic and recreational value and is protected and saved so that future generations can experience their presence and value.
Kenya has one of the richest avifauna diversity in Africa, with around 1100 bird species recorded (Bird committee 2009).
Kenya possesses a remarkable variety of globally important and valuable animal species. These include birds, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, fish and invertebrates.

The wildebeest annual migration: A herd of wildebeest crosses the Mara River during the great annual migration. Due to its greatness and uniqueness, this annual crossing has been dubbed the eighth wonder of the world and makes the Maasai Mara Game Reserve a “Tourist Mecca”. © Katie Hunt/flickr. Source Biodiversity Atlas
Key platforms and initiatives that focus on mammal conservation and monitoring in Kenya:
Kenya Wildlife Service (KWS)
- Website: Kenya Wildlife Service
- Focus: KWS is the government agency responsible for the conservation and management of Kenya’s wildlife, including mammals. They oversee national parks, reserves, and wildlife management areas where various mammal species are monitored. While not a specific platform for mammal trends, KWS conducts regular surveys and research on mammal populations, particularly for flagship species such as elephants, lions, rhinos, and giraffes.
- Key Functions: Wildlife monitoring, research, and data collection; wildlife conservation policies; and public education.
2. East African Wild Life Society (EAWLS)
- Website: EAWLS
- Focus: EAWLS is an environmental conservation organization that works to protect wildlife, including mammals, in East Africa. Through research, advocacy, and education, they engage in mammal conservation efforts and contribute to wildlife data collection, particularly for endangered species.
- Key Functions: Advocacy, research, and conservation initiatives for mammal species in East Africa.
3. Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) - Kenya
- Website: WCS Kenya
- Focus: WCS Kenya focuses on the conservation of wildlife in Kenya, including mammals like elephants, lions, and other large predators. They conduct extensive research, monitoring, and data collection on mammal populations and their habitats.
- Key Functions: Research on mammal populations, habitat preservation, and conservation efforts for key species such as elephants and big cats.
4. Lion Landscapes
- Website: Lion Landscapes
- Focus: Lion Landscapes is a conservation organization that focuses specifically on the conservation of lions and their habitats in Kenya and Tanzania. They collect data on lion populations, movements, and interactions with human populations. The platform offers insights into the status of mammal populations within lion conservation landscapes.
- Key Functions: Lion monitoring, community engagement, and conflict mitigation between lions and local communities.
5. The Giraffe Conservation Foundation (GCF)
- Website: Giraffe Conservation Foundation
- Focus: The GCF works specifically on giraffe conservation, which includes monitoring the population and distribution of giraffes in Kenya. They conduct surveys and research to understand giraffe numbers, movements, and threats.
- Key Functions: Giraffe population monitoring, research, and conservation education.
6. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
- Website: IUCN Red List
- Focus: While not specific to Kenya, the IUCN Red List provides a global status of mammal species, including those found in Kenya. The platform categorizes mammal species based on their conservation status (e.g., critically endangered, vulnerable, etc.), which helps inform local and international conservation policies.
- Key Functions: Global monitoring of species’ conservation status, including mammals in Kenya.
7. The Mara Predator Conservation Programme (MPCP)
- Website: Mara Predator Conservation Programme
- Focus: MPCP works to monitor and conserve predators in the Maasai Mara region, such as lions, cheetahs, leopards, and wild dogs. The program focuses on understanding predator populations and their interactions with the ecosystem.
- Key Functions: Predator population monitoring, conflict resolution with local communities, and data collection on predator behavior.
8. Wildlife Direct – Big Cats Program
- Website: Wildlife Direct
- Focus: Wildlife Direct runs a Big Cats Program that helps monitor populations of Kenya's big cats—lions, leopards, and cheetahs. Through a combination of research, technology, and community engagement, they track these species' movements and populations across different landscapes.
- Key Functions: Big cat monitoring, conservation, and public awareness campaigns.
9. Elephant Research and Conservation (Save the Elephants)
- Website: Save the Elephants
- Focus: Save the Elephants monitors elephant populations across Kenya, especially in key areas like Samburu and Tsavo. They use satellite collars and other technologies to track elephant movements and understand their interactions with human activities.
- Key Functions: Elephant monitoring, research, and conservation initiatives aimed at reducing human-wildlife conflict and protecting elephant habitats.

